1 2 3 4 5
6 7 8 9
com usb
1 == 1 (5V)
3 == 3 (D+)
4 == 4
7 == 2 (D-)
8 == 5 (GND)
1 2 3 4 5
6 7 8 9
com usb
1 == 1 (5V)
3 == 3 (D+)
4 == 4
7 == 2 (D-)
8 == 5 (GND)
[ VPS ] — [ NET ] —- [ NAT ] — [ UNIFI ACCESSPOINTS ]
If You can connect only one AP at time to newly created site on Your Unifi VM controller, and AP from NAT network connect to VPS f.g.
check if You have:
net.ipv4.tcp_tw_recycle = 1
in /etc/sysctl.conf
and revert it to
net.ipv4.tcp_tw_recycle = 0
Magic 😉
If Your homelab ESX have not sufficient RAM (8 GB for 6.0 and 10 GB for 6.5) is possible to pass hardware check 🙂
vCenter 6.0 – run:
installer.exe "SKIP_HARDWARE_CHECKS=1"
vCenter 6.5 – edit file:
vcsa-ui-installer\win32\resources\app\resources\layout.json
set:
"tiny": {
"cpu": 2,
"memory": 4096,
"host-count": 10,
"vm-count": 100,
"disk-swap": "25GB",
Aaaaaaand done.
Jest na trzepaku taki fajny post, ale brakuje tam configa dla Mikrotika:
https://trzepak.pl/viewtopic.php?t=51177
Wklema mój config, powycinane ma rzeczy, ale zainteresowani znajdą tu co jak wygląda.
Port eth24 nie ma mastera, jest wpięty do bridge.
eth2 = gateway
tworzymy port PPPoE, tam zapinamy neostradę na VLAN 839
NAT muscie ustawić sami.
I najważniejsze na bridge filter, jak sygnał wraca, to musi być z priorytetem 5. Inaczej TV nie gra.
PRO TIP: Jak ustawiacie router, to nie trzeba restartować dekodera 😉
Obraz pojawi się jak dobrze ustawicie sieć.
——————-
CONFIG
——————-
# aug/26/2016 by RouterOS 6.35.4 # # /interface bridge add admin-mac=00:00:00:00:00:1F auto-mac=no name=bridge-local /interface wireless /interface ethernet set [ find default-name=ether1 ] arp=disabled mac-address=00:00:00:00:00:DE name=WAN set [ find default-name=ether2 ] name=eth2 set [ find default-name=ether3 ] master-port=eth2 name=eth3 set [ find default-name=ether4 ] master-port=eth2 name=eth4 set [ find default-name=ether5 ] master-port=eth2 name=eth5 set [ find default-name=ether6 ] master-port=eth2 name=eth6 set [ find default-name=ether7 ] master-port=eth2 name=eth7 set [ find default-name=ether8 ] master-port=eth2 name=eth8 set [ find default-name=ether9 ] master-port=eth2 name=eth9 set [ find default-name=ether10 ] master-port=eth2 name=eth10 set [ find default-name=ether11 ] master-port=eth2 name=eth11 set [ find default-name=ether12 ] master-port=eth2 name=eth12 set [ find default-name=ether13 ] master-port=eth2 name=eth13 set [ find default-name=ether14 ] master-port=eth2 name=eth14 set [ find default-name=ether15 ] master-port=eth2 name=eth15 set [ find default-name=ether16 ] master-port=eth2 name=eth16 set [ find default-name=ether17 ] master-port=eth2 name=eth17 set [ find default-name=ether18 ] master-port=eth2 name=eth18 set [ find default-name=ether19 ] master-port=eth2 name=eth19 set [ find default-name=ether20 ] master-port=eth2 name=eth20 set [ find default-name=ether21 ] master-port=eth2 name=eth21 set [ find default-name=ether22 ] master-port=eth2 name=eth22 set [ find default-name=ether23 ] master-port=eth2 name=eth23 set [ find default-name=ether24 ] comment="DEKODER ORANGE" name=eth24 set [ find default-name=sfp1 ] master-port=eth2 name=sfp1-gateway /interface vlan add interface=bridge-local name=vlan1 vlan-id=1 add arp=disabled interface=WAN mtu=1492 name=vlan35 vlan-id=35 add arp=disabled interface=WAN name=vlan839 vlan-id=839 /interface pppoe-client add add-default-route=yes disabled=no interface=vlan35 max-mru=1492 max-mtu=1492 name=Orange-FTTH password=PASS user=bez_ochrony-XXXXXXXXX@neostrada.pl /ip pool add name=dhcp ranges=192.168.0.50-192.168.50.254 /ip dhcp-server add address-pool=dhcp disabled=no interface=bridge-local name=default /queue tree add name=out-queue parent=WAN queue=default add name=in-queue parent=eth2 queue=default add name=in-queue-iptv packet-mark=iptv parent=in-queue queue=default add name=out-queue-iptv packet-mark=iptv parent=out-queue queue=default /routing bgp instance set default disabled=yes /interface bridge filter add action=drop chain=forward in-interface=wlan4 add action=drop chain=forward out-interface=wlan4 add action=mark-packet chain=forward comment="Mark packets IPTV" in-interface=eth24 new-packet-mark=iptv add action=mark-packet chain=forward in-interface=vlan839 new-packet-mark=iptv add action=set-priority chain=forward comment="Set priority" in-interface=eth24 new-priority=5 out-interface=vlan839 passthrough=no add action=drop chain=forward comment="Drop not multicast" in-interface=eth24 out-interface=vlan839 packet-type=!multicast add chain=forward comment="Allow to connection to eth24" in-interface=vlan839 out-interface=eth24 add action=drop chain=forward comment="Drop any port" in-interface=vlan839 /interface bridge port add bridge=bridge-local interface=eth2 add bridge=bridge-local interface=wlan1 add bridge=bridge-local interface=wlan4 add bridge=bridge-local interface=vlan839 add bridge=bridge-local interface=eth24 /interface bridge settings set allow-fast-path=no use-ip-firewall=yes use-ip-firewall-for-vlan=yes /interface ethernet switch port set 0 per-queue-scheduling=wrr-group0:1,wrr-group0:2,wrr-group0:4,wrr-group0:8,wrr-group0:16,wrr-group0:32,wrr-group0:64,wrr-group0:128 set 1 per-queue-scheduling=wrr-group0:1,wrr-group0:2,wrr-group0:4,wrr-group0:8,wrr-group0:16,wrr-group0:32,wrr-group0:64,wrr-group0:128 set 2 per-queue-scheduling=wrr-group0:1,wrr-group0:2,wrr-group0:4,wrr-group0:8,wrr-group0:16,wrr-group0:32,wrr-group0:64,wrr-group0:128 set 3 per-queue-scheduling=wrr-group0:1,wrr-group0:2,wrr-group0:4,wrr-group0:8,wrr-group0:16,wrr-group0:32,wrr-group0:64,wrr-group0:128 set 4 per-queue-scheduling=wrr-group0:1,wrr-group0:2,wrr-group0:4,wrr-group0:8,wrr-group0:16,wrr-group0:32,wrr-group0:64,wrr-group0:128 set 5 per-queue-scheduling=wrr-group0:1,wrr-group0:2,wrr-group0:4,wrr-group0:8,wrr-group0:16,wrr-group0:32,wrr-group0:64,wrr-group0:128 set 6 per-queue-scheduling=wrr-group0:1,wrr-group0:2,wrr-group0:4,wrr-group0:8,wrr-group0:16,wrr-group0:32,wrr-group0:64,wrr-group0:128 set 7 per-queue-scheduling=wrr-group0:1,wrr-group0:2,wrr-group0:4,wrr-group0:8,wrr-group0:16,wrr-group0:32,wrr-group0:64,wrr-group0:128 set 8 per-queue-scheduling=wrr-group0:1,wrr-group0:2,wrr-group0:4,wrr-group0:8,wrr-group0:16,wrr-group0:32,wrr-group0:64,wrr-group0:128 set 9 per-queue-scheduling=wrr-group0:1,wrr-group0:2,wrr-group0:4,wrr-group0:8,wrr-group0:16,wrr-group0:32,wrr-group0:64,wrr-group0:128 set 10 per-queue-scheduling=wrr-group0:1,wrr-group0:2,wrr-group0:4,wrr-group0:8,wrr-group0:16,wrr-group0:32,wrr-group0:64,wrr-group0:128 set 11 per-queue-scheduling=wrr-group0:1,wrr-group0:2,wrr-group0:4,wrr-group0:8,wrr-group0:16,wrr-group0:32,wrr-group0:64,wrr-group0:128 set 12 per-queue-scheduling=wrr-group0:1,wrr-group0:2,wrr-group0:4,wrr-group0:8,wrr-group0:16,wrr-group0:32,wrr-group0:64,wrr-group0:128 set 13 per-queue-scheduling=wrr-group0:1,wrr-group0:2,wrr-group0:4,wrr-group0:8,wrr-group0:16,wrr-group0:32,wrr-group0:64,wrr-group0:128 set 14 per-queue-scheduling=wrr-group0:1,wrr-group0:2,wrr-group0:4,wrr-group0:8,wrr-group0:16,wrr-group0:32,wrr-group0:64,wrr-group0:128 set 15 per-queue-scheduling=wrr-group0:1,wrr-group0:2,wrr-group0:4,wrr-group0:8,wrr-group0:16,wrr-group0:32,wrr-group0:64,wrr-group0:128 set 16 per-queue-scheduling=wrr-group0:1,wrr-group0:2,wrr-group0:4,wrr-group0:8,wrr-group0:16,wrr-group0:32,wrr-group0:64,wrr-group0:128 set 17 per-queue-scheduling=wrr-group0:1,wrr-group0:2,wrr-group0:4,wrr-group0:8,wrr-group0:16,wrr-group0:32,wrr-group0:64,wrr-group0:128 set 18 per-queue-scheduling=wrr-group0:1,wrr-group0:2,wrr-group0:4,wrr-group0:8,wrr-group0:16,wrr-group0:32,wrr-group0:64,wrr-group0:128 set 19 per-queue-scheduling=wrr-group0:1,wrr-group0:2,wrr-group0:4,wrr-group0:8,wrr-group0:16,wrr-group0:32,wrr-group0:64,wrr-group0:128 set 20 per-queue-scheduling=wrr-group0:1,wrr-group0:2,wrr-group0:4,wrr-group0:8,wrr-group0:16,wrr-group0:32,wrr-group0:64,wrr-group0:128 set 21 per-queue-scheduling=wrr-group0:1,wrr-group0:2,wrr-group0:4,wrr-group0:8,wrr-group0:16,wrr-group0:32,wrr-group0:64,wrr-group0:128 set 22 per-queue-scheduling=wrr-group0:1,wrr-group0:2,wrr-group0:4,wrr-group0:8,wrr-group0:16,wrr-group0:32,wrr-group0:64,wrr-group0:128 set 23 per-queue-scheduling=wrr-group0:1,wrr-group0:2,wrr-group0:4,wrr-group0:8,wrr-group0:16,wrr-group0:32,wrr-group0:64,wrr-group0:128 set 24 per-queue-scheduling=wrr-group0:1,wrr-group0:2,wrr-group0:4,wrr-group0:8,wrr-group0:16,wrr-group0:32,wrr-group0:64,wrr-group0:128 set 25 per-queue-scheduling=wrr-group0:1,wrr-group0:2,wrr-group0:4,wrr-group0:8,wrr-group0:16,wrr-group0:32,wrr-group0:64,wrr-group0:128 /ip address add address=192.168.0.100/22 comment=LAN interface=bridge-local network=192.168.0.0 /ip cloud set ddns-enabled=yes /ip dhcp-client add comment="default configuration" dhcp-options=hostname,clientid interface=WAN /ip dhcp-server network add address=192.168.0.0/22 boot-file-name=pxelinux.0 comment="default configuration" dns-server=192.168.0.100 gateway=192.168.0.100 netmask=22 next-server=\ 192.168.0.20 ntp-server=149.156.44.126 wins-server=0.0.0.0 /ip dns set allow-remote-requests=yes servers=8.8.8.8,8.8.4.4 /ip dns static /ip firewall address-list /ip firewall filter /ip firewall service-port set irc disabled=yes /ip service set telnet disabled=yes set ftp disabled=yes set ssh address=0.0.0.0/0
—————— PONIŻEJ, BACKUP, JAK COŚ: ——————
Oferta światłowodowa Orange FTTH Triple Play składa się z usług: internet, iptv (tv+vod), voip. Aktualnie świadczone są z wykorzystaniem routerów Funbox2 lub Livebox3, w topologii pokazanej poniżej:
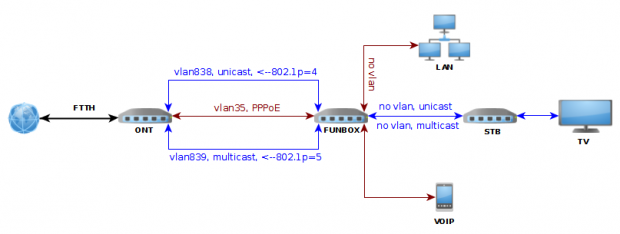
Opis instalacji sprzętowej można znaleźć na blogu Micrology:
http://www.micrology.pl/2015/04/04/swiatlowod-od-orange-ftth
http://www.micrology.pl/2015/04/06/oran … funbox-2-0
Istnieje możliwość rezygnacji z dostarczonego przez Orange routera, przy zachowaniu dostępu do wszystkich, lub prawie wszystkich usług.
WARIANT I
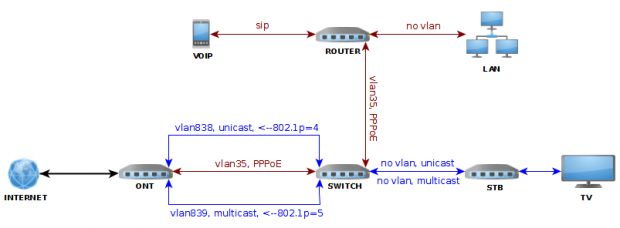
Konfiguracja odzwierciedla oryginalne ustawienia dla firmware Funbox2:
– SG10_sip-pl-5.9.13.17SoftAtHome
– FunBox2 step5.2
TELEWIZJA
Usługi IPTV składają się z:
– streaming tv + channel zapping: VLAN ID=839, multicast
– streaming vod, program tv, zegar na wyświetlaczu STB: VLAN ID=838, unicast
Ruch między ONT a swichem jest w całości tagowany vlan. Ruch między Switchem a STB jest w całości nietagowany. Ramki wychodzące z STB w stronę ONT będą na switchu tagowane vlan id wraz z priorytetem 802.1p, tj:
– dla vlan838: 802.1p=4
– dla vlan839: 802.1p=5
Przełączanie kanałów tv odbywa się w oparciu o dołączanie do i opuszczanie grup multicastowych. Szczegółowa konfiguracja zaprezentowana w oparciu o smart switch Zyxel GS1920
1. Przypisujemy porty do vlanów i podpinamy kable do urządzeń, wg wzoru:
port20 –> ONT: vlan838 tagging, vlan839 tagging, vlan35 tagging
port21 –> STB: vlan838 untagged, vlan839 untagged
port22 –> router: vlan35 tagging
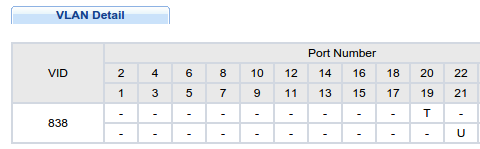
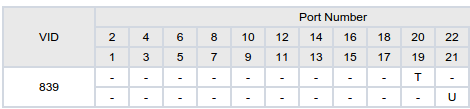
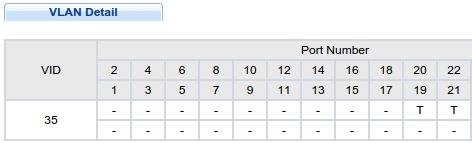
2. Cały ruch ingress na porcie 21 (do CPU switcha) będzie tagowany PVID=100 (dowolne ID inne niż domyślny management PVID=1)
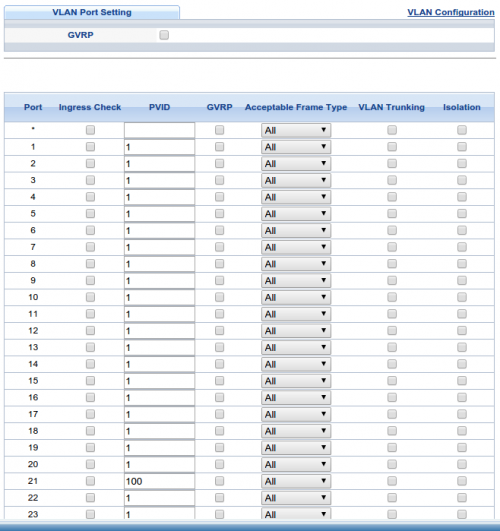
3. Definiujemy specyficzne kryteria filtrowania ruchu ingress na porcie 21 tzw. klasyfikatory
– ramki multicast igmp zostaną sklasyfikowane: protokół igmp, waga 11 (wyższy priorytet), pod nazwą „v839igmp”
– ramki unicast (tj. wszystkie inne niż wyżej wskazane multicast) zostaną sklasyfikowane: waga 10 (niższy priorytet), pod nazwą „v838all”
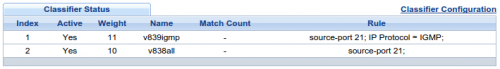
4. Priorytety klasyfikatorów za pomocą wag (wyższa waga = większy priorytet) będą ustalane manualnie
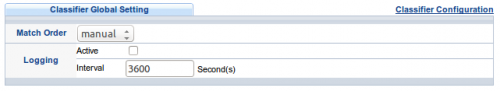
5. Definiujemy politykę dla klasyfikatora „v838all”: ustaw vlan id 838 oraz priorytet 802.1p=4
Wskazane ramki będą opuszczać switch portem nr 20 w stronę ONT
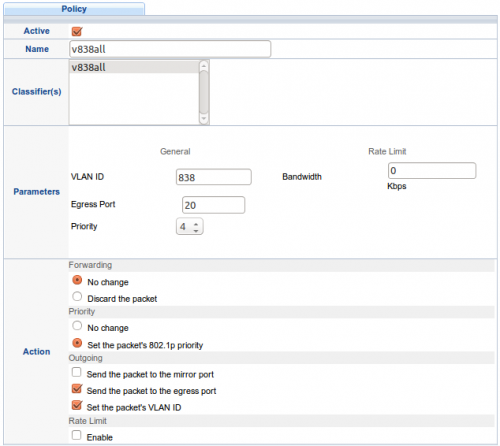
6. Definiujemy politykę dla klasyfikatora „v839igmp”: ustaw vlan id 839 oraz priorytet 802.1p=5
Wskazane ramki będą opuszczać switch portem nr 20 w stronę ONT
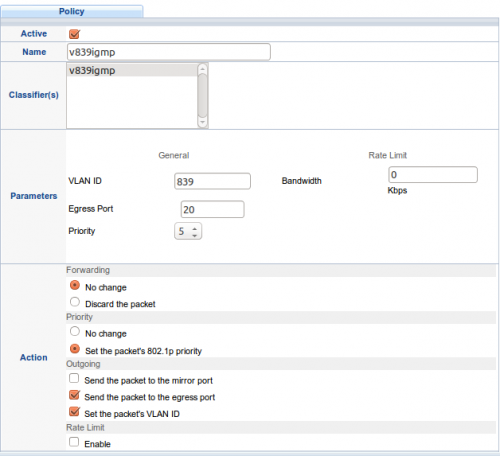
INTERNET
1. Internet dostarczany jest na VLAN ID=35
2. Autoryzacja PPPoE odbywa się w oparciu o:
login: *******@neostrada.pl/ipv6
hasło: *******
MTU: 1492 (patrz także komentarze poniżej)
Istnieje możliwość zastosowania alternatywnego loginu w postaci:
*******@neostrada.pl – protokół ipv4, zablokowane porty: 25, 135, 137, 138, 139, 445
podstawowy-*******@neostrada.pl – protokół ipv4, zablokowane porty: 135, 137, 138, 139, 445
bez_ochrony-*******@neostrada.pl – protokół ipv4, odblokowane wszystkie porty poza przeznaczonymi na provisioning
Dostawienie sufiksu /ipv6 do loginu powoduje przełączenie na protokół ipv6.
W przypadku konieczności odzyskania hasła i dostępu do konta Orange:
login: rejestracja@neostrada.pl
hasło: rejestracja
Zgodnie z zaproponowanym powyżej przykładem skonfigurowany port WAN routera łączymy z portem 22 na switchu.
VOIP
Istnieje możliwość dokonania jednoczesnej rejestracji do 5 klientów SIP (softphone, bramka voip etc) na łączu dowolnego operatora. Rozmowa przychodząca będzie zestawiana z klientem, który jako pierwszy odbierze połączenie.
Wprawdzie Orange ruch VOIP wychodzący z Funbox taguje vlan35 oraz priorytetem 802.1p=5 (a zatem dba o jakość połączenia nawet przy dużym ruchu internetowym), to konfigurację na własnych klientach SIP i dostawcach internetu wystarczy zrobić w oparciu o parametry:
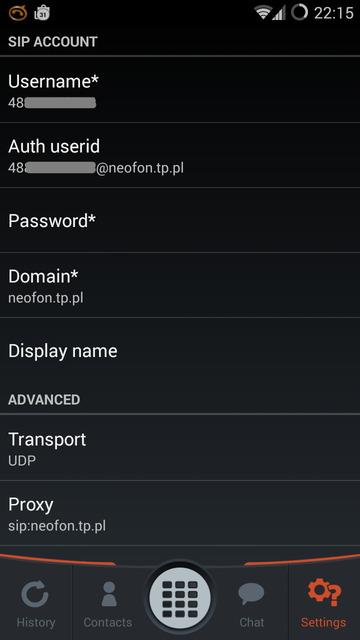
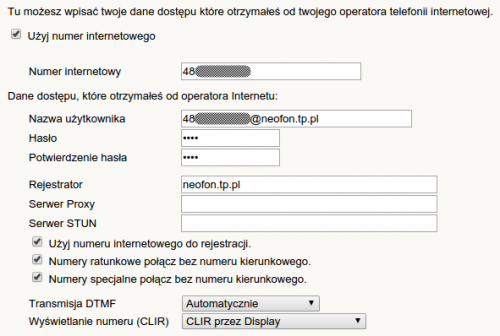
login (numer telefonu): 48*********
hasło: ********
auth userid: 48*********@neofon.tp.pl
domena/proxy: neofon.tp.pl
Przykład konfiguracji Linphone (android):
Przykład konfiguracji bramki SIP Fritzbox W701V:
WARIANT II
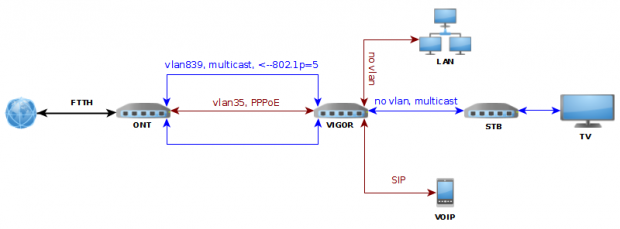
Powyższy schemat prezentuje transmisję tv (vlan 839). Konfiguracja zaprezentowana w oparciu o router Draytek Vigor 3900: firmware 121_Beta_r6132 (lub nowszy) oraz tutorial udostępniony przez producenta.
Ustawienie dostępu do internetu oraz telefonii internetowej należy wykonać wg instrukcji podanych dla wariantu I. Dostęp do telewizji będzie ograniczony do jednego, wybranego strumienia iptv (tv lub vod) ze względu na możliwości sprzętowe tego konkretnego routera tj. na pojedynczym porcie LAN tylko jeden vlan może być nietagowany.
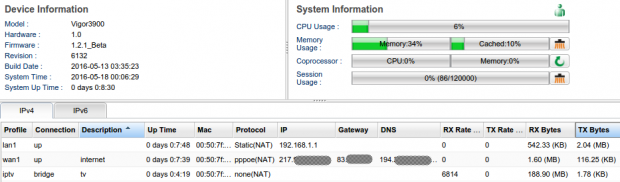
Ustanowienie interfejsu bridge (transmisja multicast) jak w przykładzie powyżej nie powoduje istotnego obciążenia CPU routera.
WARIANT III
Ten wariant zakłada:
– dostęp do wszystkich usług (w odróżnieniu od wariantu II, gdzie serwowana jest zamiennie tv lub vod)
– pierwszym urządzeniem za ONT będzie router (w odróżnieniu od wariantu I, gdzie w tym miejscu znalazł się smart switch)
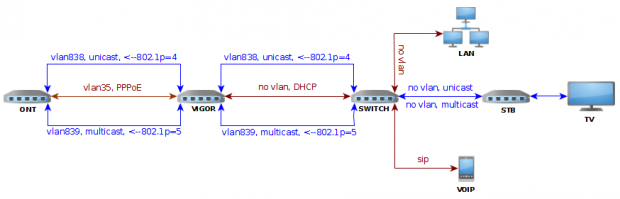
Konfiguracja zaprezentowana w oparciu o router Draytek Vigor 3900, smart switch Zyxel GS1920 oraz informacje zawarte w wariancie I oraz II. Router tym razem pełni rolę mostu dla obu vlan`ów iptv (838, 839) i przesyła ruch tagowany dalej do smart switcha.
Problem: brak transmisji tv (multicast), vod (unicast) działa
–> na routerze i/lub switchu wyłączyć opcje „multicast storm defense” lub ustawić odpowiedni próg dla transmisji danych multicast.
Problem: porty router – switch, na których przesyłany jest ruch iptv dezaktywują się
–> ponieważ router ze switchem połączony jest podwójnie (dwa kable dla: ruch internet, ruch iptv), switch może wykryć pętlę i dokonać dezaktywacji wybranego portu. Na switchu należy wyłączyć opcję „loop guard”.
Problem: usługa voip nie działa, brak głosu lub transmisja audio jednokierunkowa
–> na routerze wyłączyć opcję SIP ALG, która nierzadko jest niepoprawnie implementowana przez producentów w firmware routera.
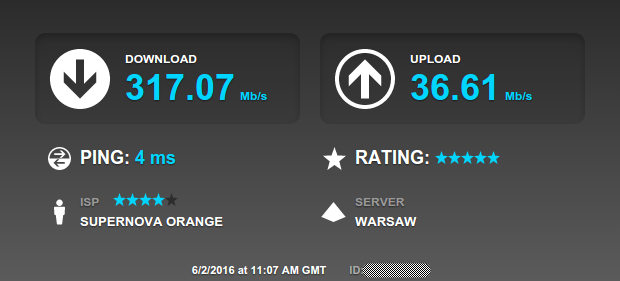
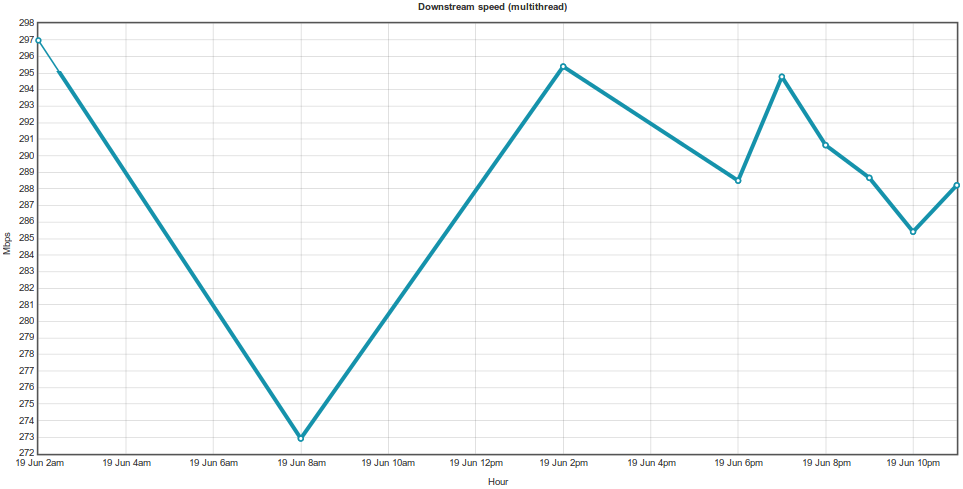
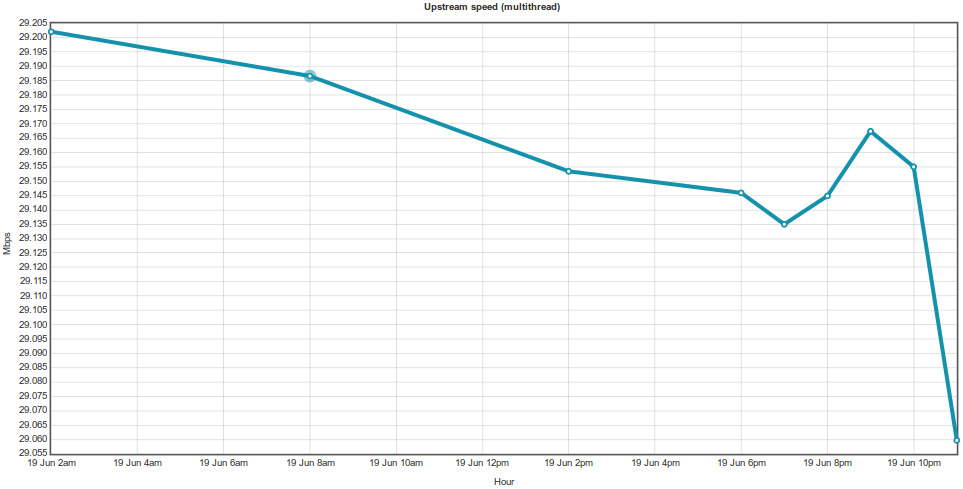
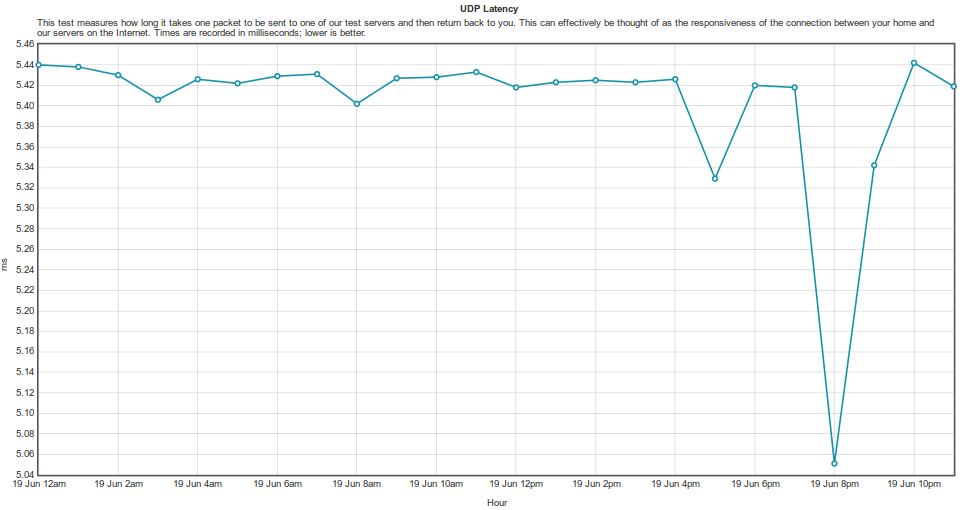
WYDAJNOŚĆ
Wszystkie testy przeprowadzone dla konfiguracji przedstawionej w wariancie III. Vigor 3900 bazuje na Linux OS, nie miał problemów z wysyceniem łącza (ustawienia domyślne firewall, włączona ochrona DDoS).
SPEEDTEST.NET
PANEL SAMKNOWS
WARIANT IV
Dostęp do wszystkich usług można również uzyskać konfigurując własny serwer Linux:
http://www.micrology.pl/2015/04/17/iptv-od-orange-ftth-na-wlasnym-routerze-zamiast-funbox-lub-livebox
http://www.micrology.pl/2016/07/17/orange-ftth-wlasny-sprzet-pelna-predkosc
FUNBOX: BŁĘDY KOMUNIKACJI
Patrz komentarze poniżej.
boot into recovery mode (grub)
aptitude purge snoopy
wget http://docs.avagotech.com/docs-and-downloads/docs-and-downloads/raid-controllers/raid-controllers-common- files/VMW-ESX-5.5.0-lsiprovider-500.04.V0.58-0006-3293953.zip unzip VMW-ESX-5.5.0-lsiprovider-500.04.V0.58-0006-3293953.zip cp vmware-esx-provider-lsiprovider.vib /tmp/ esxcli software vib install -v /tmp/vmware-esx-provider-lsiprovider.vib --no-sig-check
Configure Mikrotik as described:
/interface ipip
add comment="" disabled=no local-address=221.221.XX.XX mtu=1460 name=ipip1 \
remote-address=24.19.XX.XX
/ip address
add address=169.254.255.9/30 broadcast=169.254.255.11 comment="" disabled=no \
interface=ipip1 network=169.254.255.10
/ip ipsec peer
add address=24.19.XX.XX/32:500 auth-method=pre-shared-key comment="" \
dh-group=modp1024 disabled=no dpd-interval=30s dpd-maximum-failures=5 \
enc-algorithm=aes-128 exchange-mode=main generate-policy=no \
hash-algorithm=sha1 lifebytes=0 lifetime=1d nat-traversal=no \
proposal-check=obey secret=SECRETKEY send-initial-contact=no
/ip ipsec policy
add action=encrypt comment="" disabled=no dst-address=24.19.XX.XX/32:any \
ipsec-protocols=esp level=require priority=0 proposal=default protocol=\
ip-encap sa-dst-address=24.19.XX.XX sa-src-address=221.221.XX.XX \
src-address=221.221.XX.XX/32:any tunnel=no
/ip ipsec proposal
set default auth-algorithms=sha1 comment="" disabled=no enc-algorithms=\
aes-128 lifetime=30m name=default pfs-group=modp1024
Configure Cisco as described:
crypto isakmp policy 200
encr aes
authentication pre-share
group 2
lifetime 28800
crypto keyring keyring-qin
pre-shared-key address 221.221.XX.XX key SECRETKEY
crypto isakmp profile isakmp-qin
keyring keyring-qin
match identity address 221.221.XX.XX 255.255.255.255
crypto ipsec transform-set ipsec-prop-qin esp-aes esp-sha-hmac
mode transport
crypto ipsec profile ipsec-qin
set transform-set ipsec-prop-qin
set pfs group2
interface Tunnel4
ip address 169.254.255.10 255.255.255.252
ip virtual-reassembly
tunnel source FastEthernet4
tunnel destination 221.221.XX.XX
tunnel mode ipip
tunnel protection ipsec profile ipsec-qin
Source: http://forum.mikrotik.com/viewtopic.php?t=48580#p247067
#!/bin/bash
pass=`date +%s%D%N; cat /etc/hostname; uname -a; ip addr`
hash=`echo $pass | sha256sum | base64 | head -c 18`
echo "[!!] New password: "$hash
echo
service mysql stop
sleep 4
mysqld_safe --skip-grant-tables &
sleep 4
mysql -uroot -e "use mysql; update user set password=PASSWORD('$hash') where User='root'; flush privileges;"
kill -9 `pidof /bin/sh /usr/bin/mysqld_safe`
service mysql start
echo 'Done'
echo "[client]
#user=root
#password=$hash
" >> /root/.my.cnf
nano /root/.my.cnf
Source: http://codepoets.co.uk/2014/amavis-spamassassin/
The default Amavis log file will look something like :
Mar 23 06:48:18 my.server /usr/sbin/amavisd-new[13368]: (13368-03) Passed CLEAN {RelayedInbound}, [client.ip.addr]:37490 [client.ip.addr] -> <someone@local>, Queue-ID: 3FDEC181A06, Message-ID: <c72c5e1d26a048c0af4be75044e1e80e@bazarchic-invitations.com>
, mail_id: d-dsS6ecM4vR, Hits: -9.49, size: 34124, queued_as: 80D4118089F, dkim_sd=20132014:bazarchic-invitations.com, 3203 ms
Which isn’t all that useful – especially if you need to know WHY it did (or didn’t) score against SpamAssassin (i.e. WHY was it -9.49).
So, to make Amavis more verbose in logging – so you can see which SpamAssassin tests triggered etc – add to /etc/amavis/conf.d/50-user (debian) –
$log_templ = $log_verbose_templ;
Now you’ll see something more like :
Mar 28 14:33:49 my.server /usr/sbin/amavisd-new[9149]: (09149-05) Passed SPAMMY {RelayedTaggedInbound}, [client.ip.addr]:62696 [client.ip.addr] <some.user@whatever> -> <someone@else.example.com>, Queue-ID: EF4F4180E71, Message-ID: <C46A064E2A2B52469C092EE761AD74602BFCCC@xxxxxx-Exch.xxxxxxx.xxxx>, mail_id: dzG4JS_4jH29, Hits: 6.314, size: 46717, queued_as: BBEB71819B4, Subject: "hello world this is a subject", From: Test_Person_<test@my.domain>, helo=whatever.server, Tests: [HTML_MESSAGE=0.001,LOCAL_SEX=5,URI_HEX=1.313], shortcircuit=no, autolearn=disabled, autolearnscore=6.314, asn=AS57307_188.227.240.0/21, 4714 ms
Now – you can clearly see why it scored 6.314 – without needing to find the mail and read it’s headers.
The best for me mysql dump script,
it can be configured by cron dates,
create backup many times per day, and store fore one week.
CRON:
0 0,6,12,18 * * * /backup/mysql/backup-mysql-all-separate.sh
SCRIPT:
#!/bin/bash
OUTPUT="/backup/mysql/`date +%a/hour_%H`"
echo $OUTPUT
# if not exists
if [ ! -d "$OUTPUT" ]; then mkdir -p $OUTPUT; fi
# /bin/rm -f -v "$OUTPUT/*.gz" > /dev/null 2>&1
/bin/rm -f -v $OUTPUT/*.gz
databases=`/usr/bin/mysql -e "SHOW DATABASES;" | tr -d "| " | grep -v Database`
for db in $databases; do
if [[ "$db" != "information_schema" ]] && [[ "$db" != _* ]] && [[ "$db" != "performance_schema" ]] ; then
echo "Dumping database: $db"
/usr/bin/mysqldump --force --opt --events --databases $db > $OUTPUT/$db.sql
/bin/nice -n +19 /usr/bin/ionice -c3 /bin/gzip -9 $OUTPUT/$db.sql
fi
done